CMC is usually an anionic polymer compound prepared by reacting natural cellulose with caustic alkali and monochloroacetic acid. The molecular weight of the compound ranges from several thousand to one million. The unit structure of the molecule is shown in the figure.
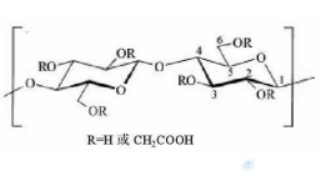
CMC is a modification of natural cellulose. At present, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have officially called it "modified cellulose." The synthesis method of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was invented by the German E. Jansen in 1918 and was granted a patent in 1921 and was seen in the world. Since then, commercial production has been realized in Europe.
CMC was only a crude product at that time, used as a colloid and adhesive. From 1936 to 1941, the industrial application research of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose was very active, and several instructive patents were published. During the Second World War, Germany used CMC in synthetic detergents as an anti-redeposition agent. And as a substitute for some natural gums (such as gelatin, gum arabic), the CMC industry has significantly been developed.
The American Hercules company started the industrial production of CMC in 1943 and produced refined sodium carboxymethyl cellulose products in 1946, which was recognized as a safe food additive.
CMC has many unique properties, such as thickening, bonding, film formation, water retention, emulsification, suspension, etc., and it is non-toxic, odorless, challenging to ferment. Good thermal stability, so it is widely used in petroleum and geology. , Daily chemical, food, medicine, and other industries, known as "industrial monosodium glutamate."
CMC is a white or slightly yellow powder, granular or fibrous solid. It is a macromolecular chemical substance that can absorb water and swell. When swelled in water, it can form a transparent viscous glue. The pH of the water suspension is 6.5-8.5. The substance is insoluble in organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, acetone, and chloroform.
Solid CMC is relatively stable to light and room temperature and stored for a long time in a dry environment. CMC is a kind of cellulose ether. It is usually made of short cotton linter (with a cellulose content of up to 98%) or wood pulp as the raw material, processed by sodium hydroxide, and then reacted with sodium monochloroacetate. The molecular weight of the compound is 6400 (± 1000). There are usually two preparation methods: the coal-water method and the solvent method. There are also other plant fibers used to make CMC.
CMC is a good emulsion stabilizer and thickener in food applications and has excellent freezing and melting stability, and can improve the flavor of the product and extend the storage time.
In 1974, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) approved pure CMC for food after rigorous biological and toxicological studies and experiments. The international standard safe intake (ADI) is 25mg/ kg body weight/day.
The thixotropic CMC plays an essential role in the gelling system and can be used to make jelly, jam, and other foods.
CMC is a kind of polyelectrolyte. It may participate in the reactions that maintain the balance of the wine body in the wine. At the same time, it combines with crystals to change the structure of the crystals and change the conditions of the crystals in the wine, causing the coagulation of the residue.